
In February 1965 Dieter Conrad, a German constitutional scholar asked his audience if the Indian Parliament could ‘…abolish Article 21, to the effect that forthwith a person could be deprived of his life or personal liberty without authorisation by law?’ Conrad was speaking at the Law Faculty, Banaras Hindu University as part of his India lecture tour. ‘Could the ruling party’, he continued, ‘if it sees its majority shrinking, amend Article 368 to the effect that the amending power rests with the president acting on the advice of the prime minister?’
Conrad presented these as ‘fictive’ scenarios to understand the true nature of constitutional concepts. However, it is possible that Conrad did not view these scenarios as completely hypothetical—his experiences in Germany informed his views on the importance of limiting the power to amend the Constitution. An unrestricted amendment power, for Conrad, was a critical path by which Hitler and the Nazis took on absolute power in Germany.
The Enabling Act of 1933 was a key moment in the rise of the Nazi Party in Germany and the consolidation of their power. The Act, passed by the German Parliament on March 23, 1933 was drafted invoking the Parliament’s amending power of the Weimar Constitution.
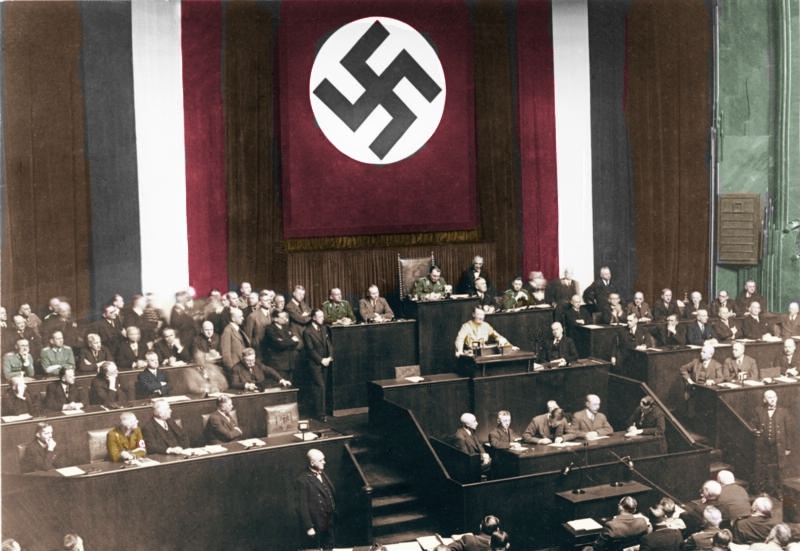
Image Credit: Wikimedia Commons
The Act was a key piece of legislation that gave the Nazi Party and Adolf Hitler sweeping powers to pass laws and make changes to the German Constitution without the input or consent of the Reichstag (the German parliament). Many civil liberties were suspended and the concentration of power in the hands of the Nazi Party ultimately resulting in the atrocities of the Holocaust and World War II. The Act effectively dispatched the Weimar Constitution to the grave, and proved to be a historical example of how a provision of the Constitution was used to bury itself.
In response to this, the framers of the 1949 German Constitution included Article 79 (3) to prevent any amendments to the Constitution that would undermine the fundamental principles of the Basic Law or the federal structure of the German state. This was seen as an important step in ensuring that the abuses of power that marked the Nazi era could not be repeated in the future.
About three months before Conrad’s speech at Banaras University, the Supreme Court of India in Sajjan Singh v. State of Rajasthan, 1964 held that Parliament could change any part of the Constitution as it pleased. It held that this power was vested in Article 368 of the Constitution, which gave the Parliament the power to amend the Constitution. The next decade was punctuated with a string of constitutional cases in which the extent of parliament’s power to amend the Constitution were debated. These cases often involved challenges to land redistribution.

Image Credit: South Asia Institute, Heidelberg University
This culminated in the Kesavananda Bharati v. State of Kerala, 1973 case, where the Indian Supreme Court ruled that Article 368 of the Indian Constitution did not extend to its basic structure. Dieter Conrad’s arguments featured prominently in this case.
Since then, the idea that parliament could not change some parts of the Constitution has been largely accepted, albeit with some episodic resistance from various quarters. But there never was a serious attack on the doctrine. Until now.
On 7 December 2022, Vice President Jagdeep Dhankar declared that ‘Parliament is the exclusive and ultimate determinative of the architecture of the Constitution’. On a different occasion, he insisted that, ‘the basic structure is primacy of the will of the people’.
Contrary to the Vice President’ s beliefs, India’s Parliament is not sovereign. And we don’t need to invoke the basic structure doctrine to make this point. We just need to point to the existence of the Constitution. If our Constitution Framers believed that Parliament and all the laws it passes must be supreme, then why did they enact a Constitution to constrain the power of different authorities in the first place? Why would they include the Parliament in this list?
40 years after the Basic Structure Doctrine, it appears that we are at the beginning of the inter-institutional debate all over again. Dieter Conrad will surely figure in this legal and political jostling over the Constitution.
More blog posts

The Constituent Assembly’s Concerns over President’s Ordinance Powers
22 May 2023 • By Siddharth Jha
Last Friday, the President promulgated an ordinance overturning a significant Supreme Court judgment. Did our Constitution framers intend for the ordinance powers to be used in such a manner?
